Climate Change
Climate Change
This webpage provides a very brief overview of climate change. The NASA Global Climate Change website contains a vast amount of information on the evidence that climate change is occurring, the causes of climate change, the impacts of climate change, as well as some actions that can be done to combat climate change. Additional resources are listed at the bottom of this page.

Global warming refers to the long-term warming of the planet.
Climate change encompasses global warming, but includes a broader range of changes, including sea level rise, shrinking glaciers, accelerating ice melt in the polar regions, heat waves, and shifts in plant flowering and growth periods. This accelerated warming is caused mainly by people burning fossil fuels and putting out heat-trapping gases into the atmosphere (the greenhouse effect).
We know carbon dioxide (CO2) levels are increasing in the atmosphere, and that this increased CO2 is the primary driver of global warming. We also know that humans are responsible for these increased CO2 concentrations, and there is overwhelming consensus about this fact among scientific experts around the world.
Read more about the causes of climate change here.
What is the greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped near the surface of the Earth, thereby warming the Earth’s surface. When the sun’s energy reaches Earth’s atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space, but some of it is trapped in the atmosphere by greenhouse gases, and this results in a warming of the Earth. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and nitrous oxides.
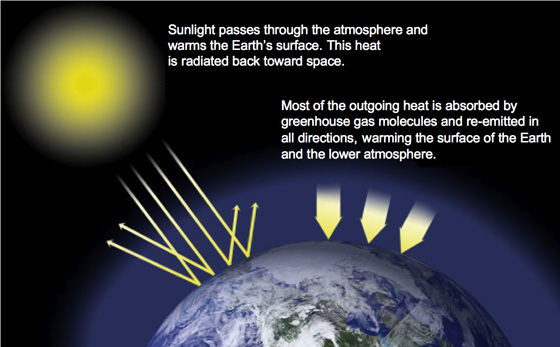
Image from NASA Global Climate Change website (www.climate.nasa.gov)
What is the difference between weather and climate?
Weather refers to the local, short term changes in the climate we see around us – rain, thunderstorms, snow, clouds, winds, heat waves and cold spells. That is, weather is local and temporary. Climate describes the average weather conditions for a region (or globally) over long period of time, such as weather conditions averaged over many years or decades. Climate is the long-term weather patterns for a region or across the globe.
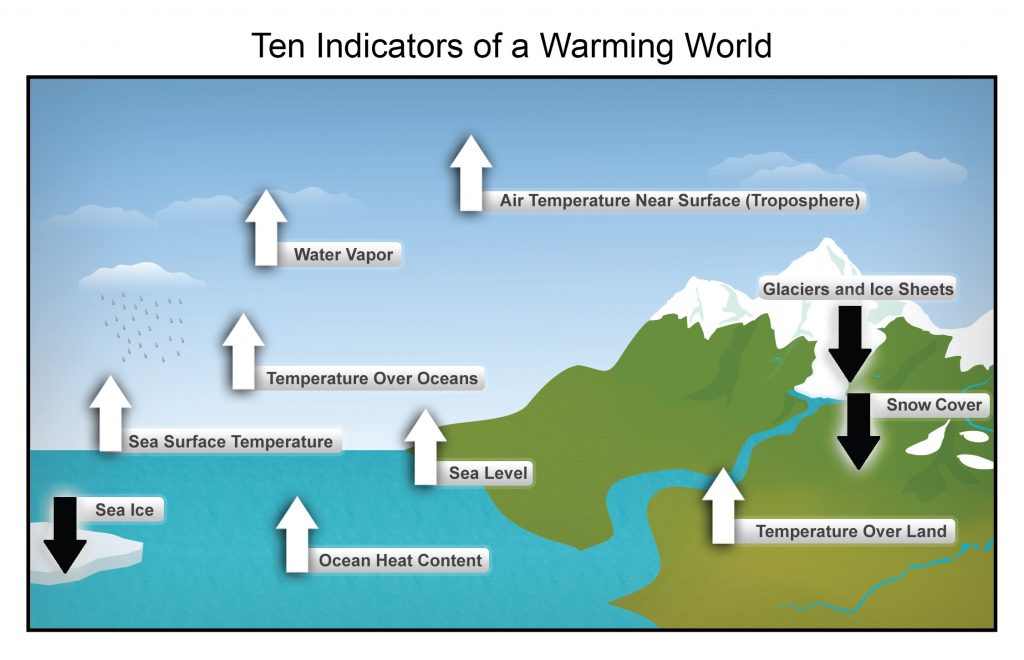
What are the effects of climate change?
- Global temperatures will rise
- Longer growing season for plants
- Heavier precipitation, which leads to greater runoff and flooding
- More droughts and water insecurity around the globe
- Longer heat waves
- Longer and more damaging wildfire seasons
- Stronger, more intense hurricanes
- Sea level rise
- Arctic Ocean will become essentially ice free in the summer months
Read more about the effects of climate change here
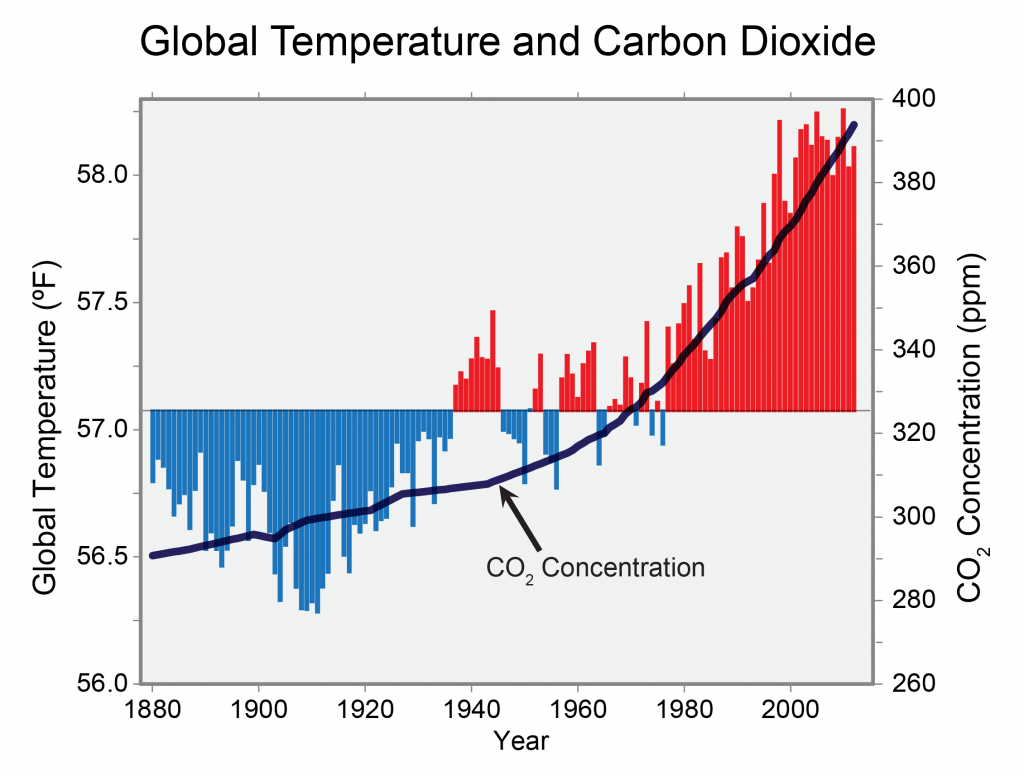
Global annual average temperatures and CO2 concentrations (1880-2012). Red bars = temperatures above the long-term average; blue bars = temperatures below that average. The black line shows atmospheric CO2 concentrations. Figure updated from Karl et al. 2009.


What can we do?
Mitigation – reducing and stabilizing the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
- Reduce emissions
- Stop deforestation
- Fight misinformation about the causes and consequences of climate change
- Prepare for unavoidable changes in climate via adaptation
Adaptation – adapting to the climate changes that are on-going or unavoidable
Read more about what we can do here.
Additional Resources:
NASA Global Climate Change website
The United States Environmental Protection Agency webpage on climate indicators
Climate Change Indicators in the United States 2016 report from the EPA
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an international group of scientists that provide a scientific basis for governments at all levels to develop climate-related policies.
The Union of Concerned Scientists has a webpage with lots of great resources
Drawdown is a great source of information – it highlights 100 solutions for reversing global warming